Page 46 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 46
During the flight between the Earth and the Moon the CSM would have to be decoupled from the Stage 3 rocket and turned around so that it could dock with the LM. Only then could the assembled spacecraft be decoupled from the Stage 3 rocket. The final spacecraft traveled with the lunar module in front.
The lunar module housed two engines. One of them could be varied in thrust to allow controlled descent to
the surface of the Moon. The other was for ascent back to the command module. The lunar module itself was made of two parts. One part was used for descent, and the other part used the descent module as a launch pad to get back into lunar orbit. This was important since nobody knew what the surface of the Moon was like, and it was essential to have a stable platform from which to lift off.
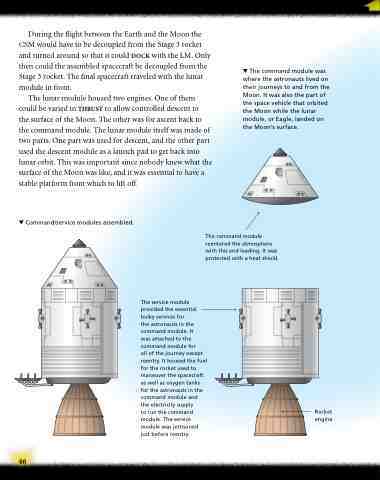
Command/service modules assembled.
The command module was where the astronauts lived on their journeys to and from the Moon. It was also the part of the space vehicle that orbited the Moon while the lunar module, or Eagle, landed on the Moon’s surface.
46
The command module reentered the atmosphere with this end leading. It was protected with a heat shield.
The service module provided the essential bulky services for
the astronauts in the command module. It
was attached to the command module for
all of the journey except reentry. It housed the fuel for the rocket used to maneuver the spacecraft as well as oxygen tanks for the astronauts in the command module and the electricity supply
to run the command module. The service module was jettisoned just before reentry.
Rocket engine