Page 11 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 11
the hydrogen atoms (which have a net positive charge). This polar property is produced from the bent shape of the molecule. The polarity (charged nature) can be demonstrated by charging up a plastic comb with static electricity (rubbing it against clothing) and then placing it close to a thin stream of water flowing from a faucet.
The stream of water will bend towards the comb, attracted by static electricity.
Hydrogen bonding
Water molecules bond to one another
in special ways. One of them is called
hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding of
water molecules gives water many properties quite unlike any other substance. It accounts for the surface tension (see page 25) effect in water as well as causing melting points (see page 17) and boiling points (see pages 14 and 20) higher than would be expected if water had properties common to other substances.
(Below) The surface tension effect of water is helped by hydrogen bonds.
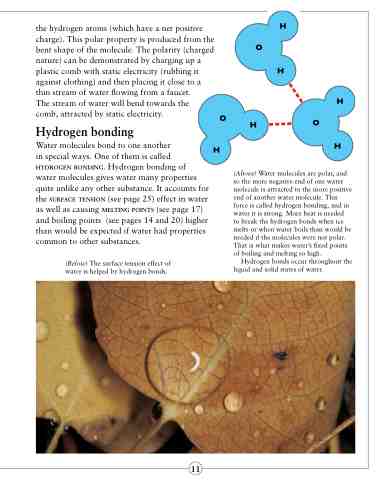
(Above) Water molecules are polar, and so the more negative end of one water molecule is attracted to the more positive end of another water molecule. This force is called hydrogen bonding, and in water it is strong. More heat is needed
to break the hydrogen bonds when ice melts or when water boils than would be needed if the molecules were not polar. That is what makes water’s fixed points of boiling and melting so high.
Hydrogen bonds occur throughout the liquid and solid states of water.
11