Page 21 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 21
allow only small ions to pass through. It is used in the electrolysis of brine.
electrolysis: an electrical–chemical process that uses an electric current to cause the break up of a compound and the movement of metal ions in a solution.
EQUATION: Electrolysis of a salt solution
alkali: a base in solution.
diaphragm: a semipermeable membrane
– a kind of ultra-fine mesh filter – that will
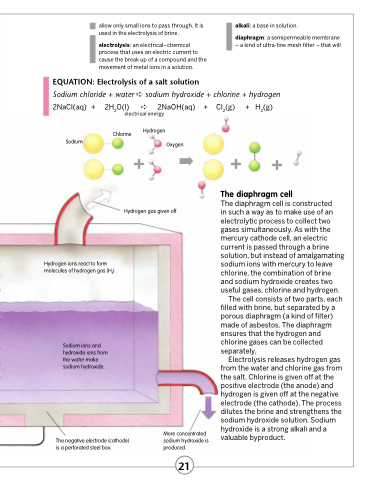
Sodium chloride + water ➪ sodium hydroxide + chlorine + hydrogen 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) ➪ 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
electrical energy
Hydrogen
Oxygen
+➡++
Sodium
Hydrogen ions react to form molecules of hydrogen gas (H2).
Sodium ions and hydroxide ions from the water make sodium hydroxide.
The negative electrode (cathode) is a perforated steel box.
More concentrated sodium hydroxide is produced.
Chlorine
Hydrogen gas given off
The diaphragm cell
The diaphragm cell is constructed
in such a way as to make use of an electrolytic process to collect two gases simultaneously. As with the mercury cathode cell, an electric current is passed through a brine solution, but instead of amalgamating sodium ions with mercury to leave chlorine, the combination of brine and sodium hydroxide creates two useful gases, chlorine and hydrogen.
The cell consists of two parts, each filled with brine, but separated by a porous diaphragm (a kind of filter) made of asbestos. The diaphragm ensures that the hydrogen and chlorine gases can be collected separately.
Electrolysis releases hydrogen gas from the water and chlorine gas from the salt. Chlorine is given off at the positive electrode (the anode) and hydrogen is given off at the negative electrode (the cathode). The process dilutes the brine and strengthens the sodium hydroxide solution. Sodium hydroxide is a strong alkali and a valuable byproduct.
21
21