Page 27 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 27
The products of nitric acid
Nitric acid reacts with a wide variety of substances. The reaction oxidises the other reagent, and reduces the nitric acid to a variety of products from nitrogen dioxide to ammonia.
Very dilute nitric acid reacts with reactive metals such as magnesium
to produce hydrogen and nitric oxide. Less reactive metals such as zinc and iron produce ammonia. Poorly reactive metals such as copper and mercury result in the production of nitric oxide or nitrogen dioxide, depending on the concentration of the acid.
A few metals, such as gold and platinum, are not affected by nitric acid. Others, such as aluminium, do not react because they are protected by their oxide coating. Hydrogen sulphide is easily oxidised by nitric acid.
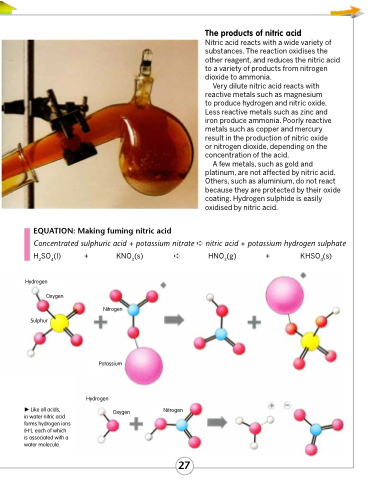
EQUATION: Making fuming nitric acid
Concentrated sulphuric acid + potassium nitrate ➪ nitric acid + potassium hydrogen sulphate
H2SO4(l)
Hydrogen Oxygen
Sulphur
+ KNO3(s) ➪
Nitrogen
Potassium
Hydrogen
HNO3(g) + KHSO4(s)
Like all acids,
in water nitric acid forms hydrogen ions (H+), each of which is associated with a water molecule.
Oxygen Nitrogen
27