Page 29 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 29
The green patina,
or surface coating, on copper statues, is made from copper carbonate.
It is popularly called verdigris and is produced as carbonic acid and oxygen in the atmosphere react with the copper. Copper roofing displays the same effect.
Also...
buffer: a chemistry term meaning a mixture of substances in solution that resists a change in the acidity or alkalinity of the solution.
weak acid: an acid that has only partly dissociated (ionised) in water. Most organic acids are weak acids.
weather: a term used by Earth scientists and derived from “weathering”, meaning to react with water and gases of the environment.
Buffer is a chemistry term meaning a mixture of substances in solution that resists a change in the acidity or alkalinity of the solution.
The purpose of a buffer is to neutralise both acids and bases.
For example, the addition of a small amount of hydrochloric acid
will add a large number of hydrogen ions to the solution. These will immediately react with buffer salts in the solution to produce an almost neutral result.
The reason many body fluids are heavily buffered with bicarbonates and carbonic acid is to keep body fluids neutral.
Bicarbonates
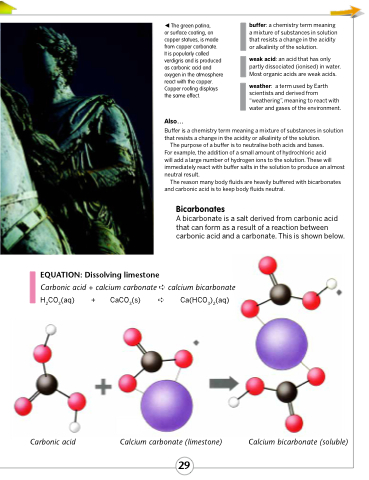
A bicarbonate is a salt derived from carbonic acid that can form as a result of a reaction between carbonic acid and a carbonate. This is shown below.
EQUATION: Dissolving limestone
Carbonic acid + calcium carbonate ➪ calcium bicarbonate H2CO3(aq) + CaCO3(s) ➪ Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
Carbonic acid Calcium carbonate (limestone) Calcium bicarbonate (soluble)
29