Page 6 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 6
Arsenic (As) Arsenic (As)
Element 33 on the periodic table. A chemical element in group 5 (the nitrogen group).
It is a non-metal common
in nature as compounds and occasionally in grey and yellow elemental form. Grey arsenic is very brittle and tarnishes in air;
the yellow form is softer. Arsenic sublimes – changing from solid
to vapour and back to solid
again without becoming a liquid in between. Arsenic is well known as
a poison. Arsenic oxide is used as
a pesticide, in adhesives and as a decoloriser in glassmaking. It is also used in the doping of silicon in integrated circuit making.
Astatine (At)
Element 85 on the periodic table. A radioactive halogen element and the heaviest member of group 7 (the halogens). It is a metalloid, is unstable and has no practical uses.
Atom
The smallest particle of an element. The ancient Greek philosopher
Democritus thought that all matter was made of atoms of what the Greeks believed to be the four elements – earth, air, fire and water. Later, it was discovered
that atoms are made of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Neutrons and protons are found in the core of the atom, called the nucleus, which contains nearly all of the mass of the atom. The total number of protons and neutrons is called the atomic mass. The number of protons in the nucleus gives the atomic number of the element, and it also equals the number of electrons in the atom.
The chemical characteristics
of elements depend on the number of electrons, and on the way in
which the atoms are arranged. Because of this, elements can be
distinguished from each other by their atomic numbers.
(See also: Fission; Fusion; Ion; Isotopes; Molecule.)
Atomic mass
The mass of an atom measured
in atomic mass units (amu). One atomic mass unit equals the mass of one-twelfth of the atom of carbon-12 (see: Carbon and Isotope). Atomic mass is now used more generally than atomic weight. The atomic mass of chlorine, for example, is about 35 amu.
(See also: Relative atomic mass.)
Atomic weight
(See: Atomic mass.) B
Barium (Ba)
Element 56 on the periodic table. One of the group 2 elements (alkaline-earth metals).
It is silvery-white when freshly cut and slightly heavier than lead.
It is mainly found as the mineral barite. This element is used in metallurgy and its compounds are used in fireworks, petroleum mining and radiology.
Barium sulphate is used as a white filler in rubber and paper. It is
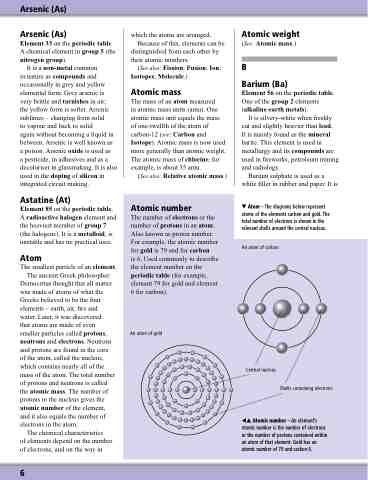
Atom – The diagrams below represent atoms of the elements carbon and gold. The total number of electrons is shown in the relevant shells around the central nucleus.
6
Atomic number
The number of electrons or the number of protons in an atom. Also known as proton number. For example, the atomic number
for gold is 79 and for carbon
is 6. Used commonly to describe the element number on the periodic table (for example, element 79 for gold and element 6 for carbon).
An atom of gold
An atom of carbon
Central nucleus
Shells containing electrons
Atomic number – An element’s atomic number is the number of electrons or the number of protons contained within an atom of that element. Gold has an atomic number of 79 and carbon 6.