Page 5 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 5
Amalgam
A liquid alloy of mercury and another metal or metals.
Americium (Am)
Element 95 on the periodic table. An artificial, silvery-white and highly radioactive metal in the actinide series.
It is also called a transuranium element because it has a higher atomic mass than uranium. It
is made from plutonium in a nuclear reactor.
Amalgam – Dental amalgam is an alloy of 52% mercury, 33% silver, 12.5% tin, 2% copper, and 0.5% zinc.
Argon (Ar)
Americium – Americium is a radioactive source used in smoke detectors.
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
Antimony (Sb)
Element 51 on the periodic table. A metalloid in group 5 (the nitrogen group) that gets its symbol from its Latin name stibium.
It is a silvery, bluish-white solid that is very brittle and has a flaky texture. It is found as a grey sulphide mineral called stibnite. Antimony is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. It tarnishes
only slightly in air, more in moist air. When heated in air, it burns with a brilliant blue flame. It has no uses as a pure metal; but
when alloyed with other metals, it makes the alloy hard and strong. Compounds of antimony are used to make materials flame- proof and as paint colourings.
Argon (Ar)
Element 18 on the periodic table. An inert (unreactive) gas and the most abundant member of group 8 (the noble gases).
It is colourless, odourless and tasteless. It was isolated in 1894, from air, by British scientists Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay.
Argon makes up about 1.3%
of the atmosphere by weight and 0.94% by volume. When electricity passes through argon, it glows pale red. It is used in light bulbs and other places where an unreactive gas is needed, for example, in the manufacture of silicon chips.
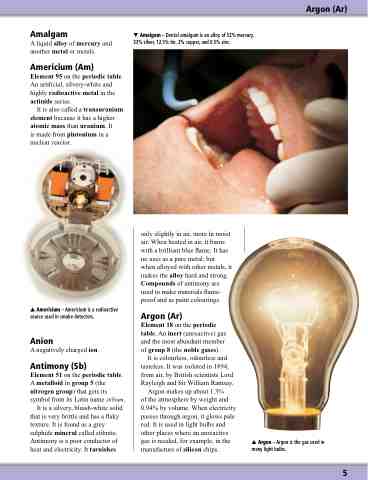
Argon – Argon is the gas used in many light bulbs.
5