Page 28 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 28
Maritime climate
M
Maritime climate
A climate that is influenced by being close to a large body
of water, usually an ocean, and that experiences onshore winds. The heat-absorbing properties of the ocean cause the range of temperatures through the year to be much smaller than in the centre of continents.
Maritime climates are noted for being mild and humid (see: Humidity). Examples are the Pacific coast of North America, northwestern Europe, southern Chile, southeastern Australia and New Zealand.
Mediterranean climate
A warm temperate coastal climate with a hot, dry summer and a mild, wet winter. The term comes from the Mediterranean region
of Europe, but similar climates
are found in southern California, central Chile, South Africa and southern Australia.
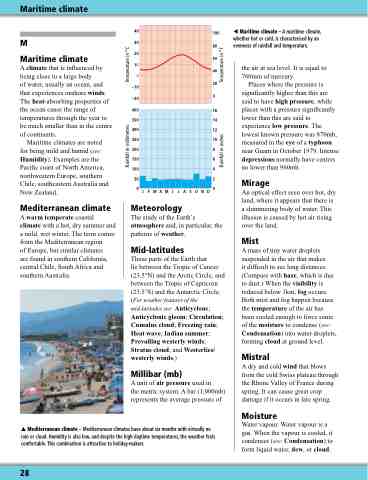
40 30 20 10
100 80 60
Maritime climate – A maritime climate, whether hot or cold, is characterised by an evenness of rainfall and temperature.
the air at sea level. It is equal to 760mm of mercury.
Places where the pressure is significantly higher than this are said to have high pressure, while places with a pressure significantly lower than this are said to experience low pressure. The lowest known pressure was 870mb, measured in the eye of a typhoon near Guam in October 1979. Intense depressions normally have centres no lower than 960mb.
Mirage
An optical effect seen over hot, dry land, where it appears that there is a shimmering body of water. This illusion is caused by hot air rising over the land.
Mist
A mass of tiny water droplets suspended in the air that makes
it difficult to see long distances. (Compare with haze, which is due to dust.) When the visibility is reduced below 1km, fog occurs. Both mist and fog happen because the temperature of the air has been cooled enough to force some of the moisture to condense (see: Condensation) into water droplets, forming cloud at ground level.
Mistral
A dry and cold wind that blows from the cold Swiss plateau through the Rhone Valley of France during spring. It can cause great crop damage if it occurs in late spring.
Moisture
Water vapour. Water vapour is a gas. When the vapour is cooled, it condenses (see: Condensation) to form liquid water, dew, or cloud.
0 40
20 –20 0
–10
400 350 300 250 200 150 100
16 14 12 10 8 6 4
50 2
0
Meteorology
0
JFMAMJJASOND
The study of the Earth’s atmosphere and, in particular, the patterns of weather.
Mid-latitudes
Those parts of the Earth that
lie between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) and the Arctic Circle, and between the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S) and the Antarctic Circle. (For weather features of the mid-latitudes see: Anticyclone; Anticyclonic gloom; Circulation; Cumulus cloud; Freezing rain; Heat wave; Indian summer; Prevailing westerly winds; Stratus cloud; and Westerlies/ westerly winds.)
Millibar (mb)
A unit of air pressure used in
the metric system. A bar (1,000mb) represents the average pressure of
Mediterranean climate – Mediterranean climates have about six months with virtually no rain or cloud. Humidity is also low, and despite the high daytime temperatures, the weather feels comfortable. This combination is attractive to holiday-makers.
28
Rainfall in millimetres Temperature in °C
Rainfall in inches Temperature in °F