Page 27 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 27
Lee, leeward
The coast or flank of a mountain sheltered from the prevailing winds. The lee side of a mountain is useful as a sheltered harbour, but it may present problems for farming, since lee sides lie in the rain shadow of mountains and so may be quite dry.
Local weather
The special weather effects that show up when the air is calm. Examples include mountain and valley winds, sea breezes and heat islands.
Low, low pressure Low, low pressure
A region in which the air pressure, as measured by
a barometer, is lower than average. Lows are places of rising air, cloud and rain and cause depressions or cyclones.
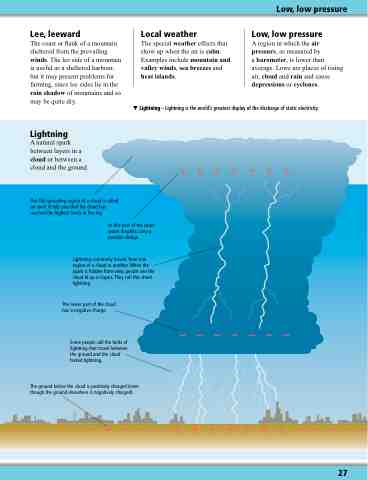
Lightning – Lightning is the world’s greatest display of the discharge of static electricity.
Lightning
A natural spark between layers in a cloud or between a cloud and the ground.
This flat spreading region of a cloud is called an anvil. It tells you that the cloud has reached the highest levels in the sky.
In this part of the cloud water droplets carry a positive charge.
Lightning commonly travels from one region of a cloud to another. When the spark is hidden from view, people see the cloud lit up in layers. They call this sheet lightning.
The lower part of the cloud has a negative charge.
Some people call the bolts of lightning that travel between the ground and the cloud forked lightning.
The ground below the cloud is positively charged (even though the ground elsewhere is negatively charged).
27