Page 51 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 51
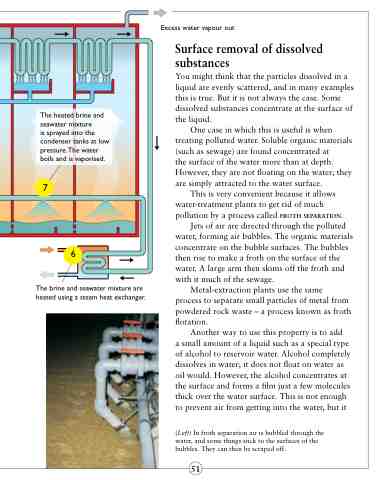
The heated brine and seawater mixture
is sprayed into the condenser tanks at low pressure.The water boils and is vaporised.
7
6
Excess water vapour out
The brine and seawater mixture are heated using a steam heat exchanger.
Surface removal of dissolved
substances
You might think that the particles dissolved in a liquid are evenly scattered, and in many examples this is true. But it is not always the case. Some dissolved substances concentrate at the surface of the liquid.
One case in which this is useful is when treating polluted water. Soluble organic materials (such as sewage) are found concentrated at
the surface of the water more than at depth. However, they are not floating on the water; they are simply attracted to the water surface.
This is very convenient because it allows water-treatment plants to get rid of much pollution by a process called froth separation.
Jets of air are directed through the polluted water, forming air bubbles. The organic materials concentrate on the bubble surfaces. The bubbles then rise to make a froth on the surface of the water. A large arm then skims off the froth and with it much of the sewage.
Metal-extraction plants use the same process to separate small particles of metal from powdered rock waste – a process known as froth flotation.
Another way to use this property is to add
a small amount of a liquid such as a special type of alcohol to reservoir water. Alcohol completely dissolves in water; it does not float on water as oil would. However, the alcohol concentrates at the surface and forms a film just a few molecules thick over the water surface. This is not enough to prevent air from getting into the water, but it
(Left) In froth separation air is bubbled through the water, and some things stick to the surfaces of the bubbles. They can then be scraped off.
51