Page 29 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 29
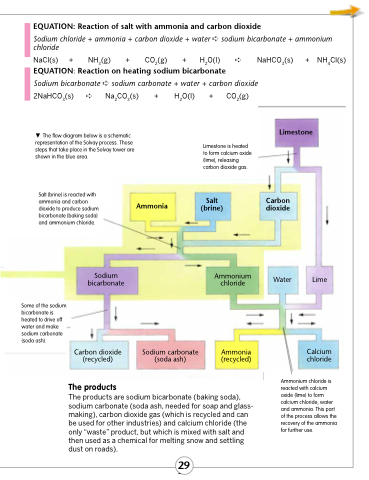
EQUATION: Reaction of salt with ammonia and carbon dioxide
Sodium chloride + ammonia + carbon dioxide + water ➪ sodium bicarbonate + ammonium chloride
NaCl(s) + NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ➪ NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(s) EQUATION: Reaction on heating sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate ➪ sodium carbonate + water + carbon dioxide
2NaHCO3(s) ➪ Na2CO3(s) +
The flow diagram below is a schematic representation of the Solvay process. Those steps that take place in the Solvay tower are shown in the blue area.
Salt (brine) is reacted with
ammonia and carbon Ammonia dioxide to produce sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda)
and ammonium chloride.
H2O(l)
+ CO2(g)
Limestone is heated to form calcium oxide (lime), releasing carbon dioxide gas.
Salt (brine)
Ammonium chloride
Ammonia (recycled)
Some of the sodium bicarbonate is heated to drive off water and make sodium carbonate (soda ash).
Sodium bicarbonate
Carbon dioxide (recycled)
The products
Carbon dioxide
Water
Lime
Calcium chloride
Limestone
Sodium carbonate (soda ash)
The products are sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), sodium carbonate (soda ash, needed for soap and glass- making), carbon dioxide gas (which is recycled and can be used for other industries) and calcium chloride (the only “waste” product, but which is mixed with salt and then used as a chemical for melting snow and settling dust on roads).
29 29
Ammonium chloride is reacted with calcium oxide (lime) to form calcium chloride, water and ammonia. This part of the process allows the recovery of the ammonia for further use.