Page 27 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 27
anode: the negative terminal of a battery or the positive ion: an atom, or group of atoms, that has gained or lost one electrode of an electrolysis cell. or more electrons and so developed an electrical charge.
brine: a solution of salt (sodium chloride) in water. membrane: a thin flexible sheet. A semipermeable
cathode: the positive terminal of a battery or the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell.
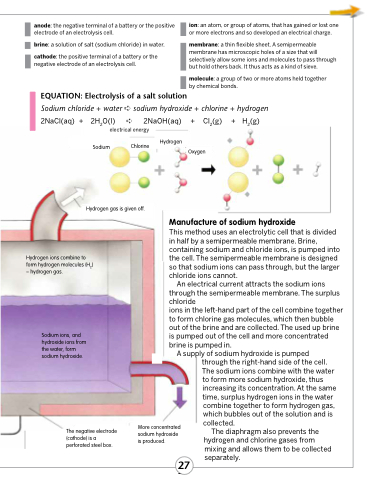
EQUATION: Electrolysis of a salt solution
membrane has microscopic holes of a size that will selectively allow some ions and molecules to pass through but hold others back. It thus acts as a kind of sieve.
molecule: a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Sodium chloride + water ➪ sodium hydroxide + chlorine + hydrogen 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) ➪ 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
electrical energy
Sodium Chlorine
Hydrogen gas is given off.
Hydrogen ions combine to form hydrogen molecules (H2) – hydrogen gas.
Sodium ions, and hydroxide ions from the water, form sodium hydroxide.
The negative electrode (cathode) is a perforated steel box.
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Manufacture of sodium hydroxide
This method uses an electrolytic cell that is divided in half by a semipermeable membrane. Brine, containing sodium and chloride ions, is pumped into the cell. The semipermeable membrane is designed so that sodium ions can pass through, but the larger chloride ions cannot.
An electrical current attracts the sodium ions through the semipermeable membrane. The surplus chloride
ions in the left-hand part of the cell combine together to form chlorine gas molecules, which then bubble out of the brine and are collected. The used up brine is pumped out of the cell and more concentrated brine is pumped in.
A supply of sodium hydroxide is pumped through the right-hand side of the cell. The sodium ions combine with the water
to form more sodium hydroxide, thus increasing its concentration. At the same time, surplus hydrogen ions in the water
combine together to form hydrogen gas, which bubbles out of the solution and is collected.
The diaphragm also prevents the hydrogen and chlorine gases from
mixing and allows them to be collected separately.
More concentrated sodium hydroxide is produced.
27 27