Page 40 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 40
Niobium (Nb)
Element 41. A soft, shiny, white and easily shaped (ductile) metal belonging to the transition metals in the Periodic Table.
It looks like steel with a bluish tinge when kept in air, but looks more like platinum when polished. It is used in alloys, in particular in some stainless steels to give extra strength.
Key facts...
Name: niobium
Symbol: Nb
Atomic number: 41
Atomic weight: 92.9
Position in Periodic Table: transition metal,
group (5) (vanadium group); period 5 State at room temperature: solid Colour: silvery-white
Density of solid: 8.57 g/cc
Melting point: 2,477°C
Boiling point: 4,744°C
Origin of name: from the Greek word
Niobe, meaning daughter of Tantalus (because it is so similar chemically to the element tantalum)
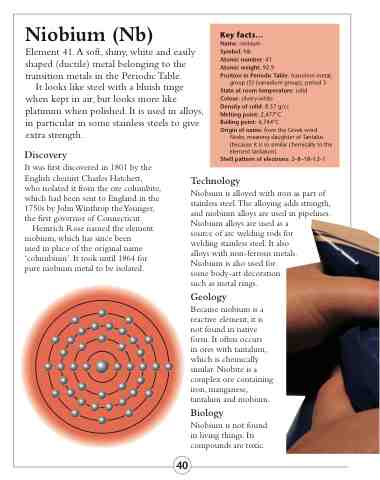
Shell pattern of electrons: 2–8–18–12–1
Discovery
It was first discovered in 1801 by the English chemist Charles Hatchett,
who isolated it from the ore columbite, which had been sent to England in the 1750s by JohnWinthrop theYounger, the first governor of Connecticut.
Heinrich Rose named the element niobium, which has since been
used in place of the original name ‘columbium’. It took until 1864 for pure niobium metal to be isolated.
Technology
Niobium is alloyed with iron as part of stainless steel.The alloying adds strength, and niobium alloys are used in pipelines. Niobium alloys are used as a
source of arc welding rods for welding stainless steel. It also alloys with non-ferrous metals. Niobium is also used for
some body-art decoration such as metal rings.
Geology
Because niobium is a reactive element, it is not found in native form. It often occurs
in ores with tantalum, which is chemically similar. Niobite is a complex ore containing iron, manganese, tantalum and niobium.
Biology
Niobium is not found in living things. Its compounds are toxic.
40