Page 39 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 39
Key facts...
Name: nickel
Symbol: Ni
Atomic number: 28
Atomic weight: 58.69
Position in Periodic Table: transition metal,
group (10) (nickel group); period 4 State at room temperature: solid Colour: silvery
Density of solid: 8.90 g/cc
Melting point: 1,453°C
Boiling point: 2,732°C
Origin of name: from the German word
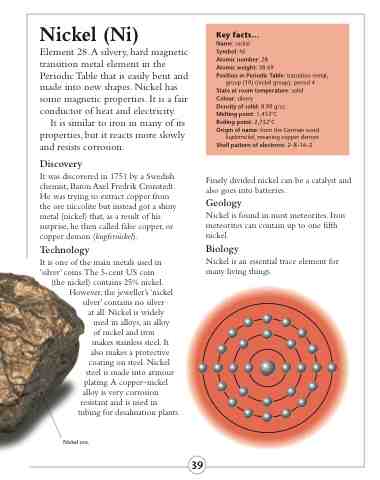
kupfernickel, meaning copper demon Shell pattern of electrons: 2–8–16–2
Nickel (Ni)
Element 28. A silvery, hard magnetic transition metal element in the Periodic Table that is easily bent and made into new shapes. Nickel has some magnetic properties. It is a fair conductor of heat and electricity.
It is similar to iron in many of its properties, but it reacts more slowly and resists corrosion.
Discovery
It was discovered in 1751 by a Swedish chemist, Baron Axel Fredrik Cronstedt. He was trying to extract copper from the ore niccolite but instead got a shiny metal (nickel) that, as a result of his surprise, he then called false copper, or copper demon (kupfernickel).
Technology
It is one of the main metals used in ‘silver’ coins.The 5-cent US coin
(the nickel) contains 25% nickel. However, the jeweller’s ‘nickel
silver’ contains no silver at all. Nickel is widely
used in alloys; an alloy
of nickel and iron makes stainless steel. It also makes a protective
coating on steel. Nickel steel is made into armour
plating.A copper–nickel alloy is very corrosion
resistant and is used in tubing for desalination plants.
Finely divided nickel can be a catalyst and also goes into batteries.
Geology
Nickel is found in most meteorites. Iron meteorites can contain up to one fifth nickel.
Biology
Nickel is an essential trace element for many living things.
Nickel ore.
39