Page 8 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 8
Arctic air Arctic air
The airstream that flows down from the Arctic Ocean. It is a cold and often raw airstream, most common in winter and often connected with rain, sleet and snow showers.
Arctic climate
A cold climate with a very brief warm season of less than three months above 6°C.
Arctic front
The region where an arctic airstream meets warmer air flowing polewards from the south.
Depressions are formed along this front.
Arctic sea smoke
Advection, or steam fog, in arctic waters. It occurs where air moving from the south flows over cold arctic waters.
Arid climate
Often called desert climates – where dryness is the overriding feature, and where plants are
very scarce. There is no special amount of rainfall that marks these climates. They are determined entirely by the amount of vegetation that can grow.
Aspect
The direction something faces. In weather terms it is most important for mountain valleys in relation
to the Sun. Places with an aspect facing the morning Sun become frost-free earlier in the day. Places with an aspect facing the setting Sun have warmer evenings.
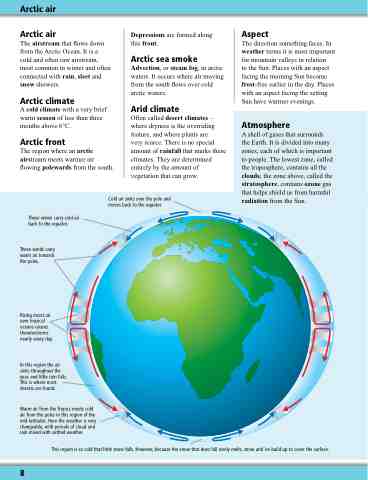
Cold air sinks over the pole and moves back to the equator.
Atmosphere
A shell of gases that surrounds the Earth. It is divided into many zones, each of which is important to people. The lowest zone, called the troposphere, contains all the clouds; the zone above, called the stratosphere, contains ozone gas that helps shield us from harmful radiation from the Sun.
These winds carry cold air back to the equator.
These winds carry warm air towards the poles.
Rising moist air over tropical oceans causes thunderstorms nearly every day.
In this region the air sinks throughout the year, and little rain falls. This is where most deserts are found.
Warm air from the Tropics meets cold air from the poles in this region of the mid-latitudes. Here the weather is very changeable, with periods of cloud and rain mixed with settled weather.
This region is so cold that little snow falls. However, because the snow that does fall rarely melts, snow and ice build up to cover the surface.
8