Page 12 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 12
City weather
City weather
The warmer conditions that exist within a city due to the shelter
of buildings and the heat produced by heating systems and vehicle exhausts. (See also: Heat island.)
Climate
The long-term, or average, kind of weather that might be expected
at a particular place over time.
To find out the climate of a
place, long-term readings are taken of temperature, rainfall, cloud formation and so on, and averages are figured out for each month. (For types of climate see individual entries.)
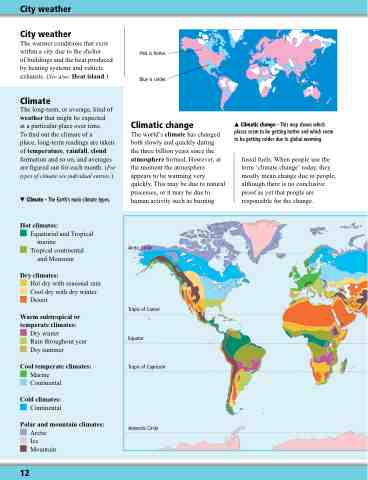
Climate – The Earth’s main climate types.
Hot climates:
Equatorial and Tropical marine
Tropical continental and Monsoon
Dry climates:
Hot dry with seasonal rain Cool dry with dry winter Desert
Warm subtropical or temperate climates:
Dry winter
Rain throughout year Dry summer
Cool temperate climates:
Marine Continental
Cold climates:
Continental
Polar and mountain climates:
Arctic Ice Mountain
Pink is hotter.
Blue is colder.
Climatic change
The world’s climate has changed both slowly and quickly during
the three billion years since the atmosphere formed. However, at the moment the atmosphere appears to be warming very quickly. This may be due to natural processes, or it may be due to human activity such as burning
Arctic Circle
Tropic of Cancer
Equator
Tropic of Capricorn
Antarctic Circle
Climatic change – This map shows which places seem to be getting hotter and which seem to be getting colder due to global warming.
fossil fuels. When people use the term ‘climate change’ today, they mostly mean change due to people, although there is no conclusive proof as yet that people are responsible for the change.
12