Page 13 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 13
astronomically so close to it.
The next closest star (Proxima Centauri) is a quarter of
a million times farther away. Because brightness decreases with the square of distance from the Earth, this star appears to be 62 billion times less bright than the Sun.
The brightness of the Sun is described by its magnitude. The lower the number, the brighter the star. From the Earth the Sun appears to have a magnitude of –26.8 and so is the brightest thing in the sky. But its absolute magnitude (the star’s true brightness if all of the stars were the same distance from Earth) is just 4.8. Thus it is, in reality, not a very bright object. By contrast, a bright star, such as Betelgeuse, has
an absolute magnitude of –9 and can be seen clearly even though it is 310 light-years away.
How the Sun moves in space
At 16° latitude the Sun spins on its axis once every 25.4 days. This is taken as the standard for solar rotation. But, because the Sun is made of fluid gas, and not solid rock like the Earth, not all of it rotates at the same speed. Gas near the poles takes 36 days to rotate.
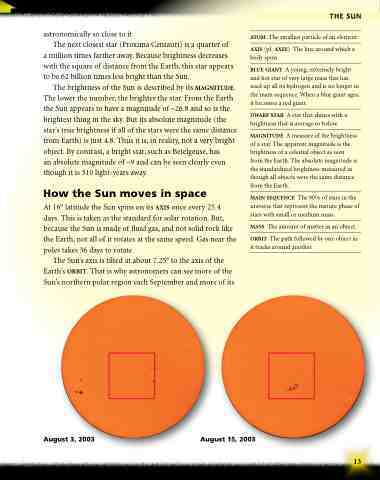
The Sun’s axis is tilted at about 7.25° to the axis of the Earth’s orbit. That is why astronomers can see more of the Sun’s northern polar region each September and more of its
atom The smallest particle of an element. axis (pl. axes) The line around which a
body spins.
blue giant A young, extremely bright and hot star of very large mass that has used up all its hydrogen and is no longer in the main sequence. When a blue giant ages, it becomes a red giant.
dwarf star A star that shines with a brightness that is average or below.
magnitude A measure of the brightness of a star. The apparent magnitude is the brightness of a celestial object as seen from the Earth. The absolute magnitude is the standardized brightness measured as though all objects were the same distance from the Earth.
main sequence The 90% of stars in the universe that represent the mature phase of stars with small or medium mass.
mass The amount of matter in an object. orbit The path followed by one object as
it tracks around another.
August 3, 2003 August 15, 2003
13