Page 56 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 56
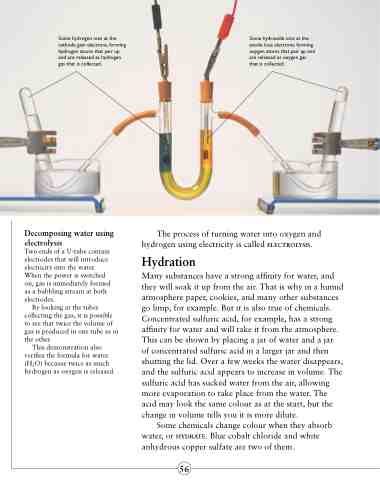
Some hydrogen ions at the cathode gain electrons, forming hydrogen atoms that pair up and are released as hydrogen gas that is collected.
Some hydroxide ions at the anode lose electrons, forming oxygen atoms that pair up and are released as oxygen gas that is collected.
Decomposing water using
electrolysis
Two ends of a U-tube contain electrodes that will introduce electricity into the water. When the power is switched on, gas is immediately formed as a bubbling stream at both electrodes.
By looking at the tubes collecting the gas, it is possible to see that twice the volume of gas is produced in one tube as in the other.
This demonstration also verifies the formula for water (H2O) because twice as much hydrogen as oxygen is released.
The process of turning water into oxygen and hydrogen using electricity is called electrolysis.
Hydration
Many substances have a strong affinity for water, and they will soak it up from the air. That is why in a humid atmosphere paper, cookies, and many other substances go limp, for example. But it is also true of chemicals. Concentrated sulfuric acid, for example, has a strong affinity for water and will take it from the atmosphere. This can be shown by placing a jar of water and a jar
of concentrated sulfuric acid in a larger jar and then shutting the lid. Over a few weeks the water disappears, and the sulfuric acid appears to increase in volume. The sulfuric acid has sucked water from the air, allowing more evaporation to take place from the water. The acid may look the same colour as at the start, but the change in volume tells you it is more dilute.
Some chemicals change colour when they absorb water, or hydrate. Blue cobalt chloride and white anhydrous copper sulfate are two of them.
56