Page 22 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 22
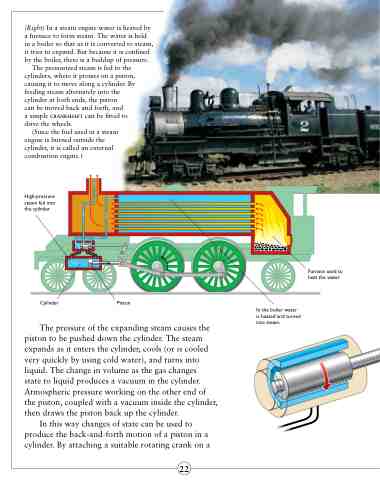
(Right) In a steam engine water is heated by a furnace to form steam. The water is held in a boiler so that as it is converted to steam, it tries to expand. But because it is confined by the boiler, there is a buildup of pressure.
The pressurized steam is fed to the cylinders, where it presses on a piston, causing it to move along a cylinder. By feeding steam alternately into the cylinder at both ends, the piston
can be moved back and forth, and a simple crankshaft can be fitted to drive the wheels.
(Since the fuel used in a steam engine is burned outside the cylinder, it is called an external combustion engine.)
High-pressure steam fed into the cylinder
Furnace used to heat the water
Cylinder
Piston
The pressure of the expanding steam causes the piston to be pushed down the cylinder. The steam expands as it enters the cylinder, cools (or is cooled very quickly by using cold water), and turns into liquid. The change in volume as the gas changes
state to liquid produces a vacuum in the cylinder. Atmospheric pressure working on the other end of the piston, coupled with a vacuum inside the cylinder, then draws the piston back up the cylinder.
In this way changes of state can be used to produce the back-and-forth motion of a piston in a cylinder. By attaching a suitable rotating crank on a
In the boiler water is heated and turned into steam.
22