Page 46 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 46
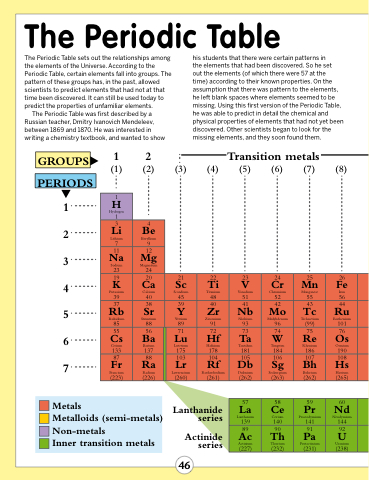
The Periodic Table
The Periodic Table sets out the relationships among the elements of the Universe. According to the Periodic Table, certain elements fall into groups. The pattern of these groups has, in the past, allowed scientists to predict elements that had not at that time been discovered. It can still be used today to predict the properties of unfamiliar elements.
The Periodic Table was first described by a Russian teacher, Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleev, between 1869 and 1870. He was interested in writing a chemistry textbook, and wanted to show
1 2
(1) (2) (3)
his students that there were certain patterns in
the elements that had been discovered. So he set
out the elements (of which there were 57 at the
time) according to their known properties. On the assumption that there was pattern to the elements, he left blank spaces where elements seemed to be missing. Using this first version of the Periodic Table, he was able to predict in detail the chemical and physical properties of elements that had not yet been discovered. Other scientists began to look for the missing elements, and they soon found them.
Transition metals
(4) (5) (6) (7) (8)
GROUPS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
PERIODS
1
H
Hydrogen 1
34
Li Be
Lithium Beryllium 79
11 12
Na Mg
Sodium Magnesium 23 24
19 20
21
22
23
K Ca
Potassium Calcium 39 40
37 38
Sc
Scandium 45
Ti
V
Titanium 48
Vanadium 51
Niobium 93
39
40
41
43
Rb Sr
Rubidium Strontium 85 88
55 56
Y
Yttrium 89
Zr
Nb
Tc
Zirconium 91
Technetium (99)
Rhenium 186
Ru
71
72
73
74
75
76
Cs Ba
Cesium Barium 133 137
Lu
Lutetium 175
103
Lr
Lawrencium (260)
Hf
Ta
Hafnium 178
Tantalum 181
104
105
Rf
Db
Rutherfordium (261)
Dubnium (262)
24
Cr
Chromium 52
Molybdenum 96
42
Mo
W
Tungsten 184
Re
26
Fe
Iron 56
Ruthenium 101
44
Os
Osmium 190
87 88
Fr Ra
Francium Radium (223) (226)
106
107
108
Sg
Seaborgium (263)
25
Mn
Manganese 55
Bh
Bohrium (262)
Hs
Hassium M (265)
57
58
Metals
Metalloids (semi-metals) Non-metals
Inner transition metals
Lanthanide series
Actinide series
La
Lanthanum 139
Ce
Cerium 140
59
Pr
Praseodymium 141
60
Nd
Neodymium Pr 144
89
Ac
46
Actinium (227)
90
Th
Thorium (232)
91
92
Pa
Protactinium (231)
U
Uranium N (238)
C
R
R
M
(
P
o (
N
(