Page 11 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 11
Refining lead by the Parkes process
In the Parkes process, contaminating elements are removed in a number of stages designed to allow the recovery of the impurities (which are themselves often valuable) as well as the lead.
Ingots of lead are melted and then allowed to cool. Copper has a higher melting point than lead, so as the mixture cools, crystals of copper float to the surface and can be skimmed off.
The lead is then reheated and a blast of air shot through it. This oxidises elements such as arsenic, and the oxides form a slag that can be skimmed off.
The next stage involves removing the silver and gold with a small amount of zinc. The silver and gold are more soluble than lead in zinc, so they alloy with the zinc. Zinc alloy is less dense that lead, so it rises to the surface and can be skimmed off. In this way zinc, silver and gold are all removed.
The remaining material, which is already nearly pure lead, can be further refined by electrolysis. An impure lead slab
is used as the anode and a pure lead slab as the cathode. As the current flows, lead ions are attracted to the cathode of the cell and electroplated on it. When the cathode has accumulated sufficient lead, it is removed and replaced. The impurities on the anode consist mainly of valuable bismuth, and they, too, are collected.
alloy: a mixture of a metal and various other elements.
electrode: a conductor that forms one terminal of a cell.
electrolysis: an electrical–chemical process that uses an electric current to cause the break up of a compound and the movement of metal ions in a solution. The process happens in many natural situations (as for example in rusting) and is also commonly used in industry for purifying (refining) metals or for plating metal objects with a fine, even metal coating.
electrolyte: a solution that conducts electricity.
gangue: the unwanted material in an ore.
oxidation: a reaction in which the oxidising agent removes electrons. (Note that oxidising agents do not have to contain oxygen.)
pyrometallurgy: refining a metal from its ore using heat. A blast furnace or smelter is the main equipment used.
slag: a mixture of substances that are waste products of a furnace. Most slags are composed mainly of silicates.
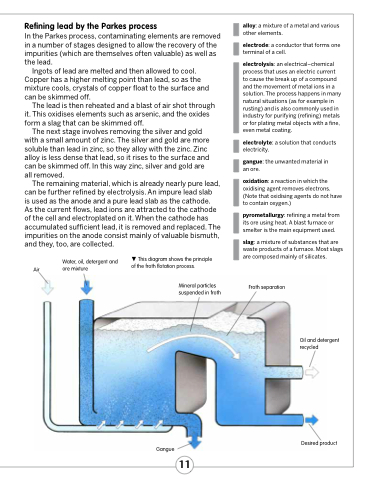
Air
Water, oil, detergent and ore mixture
This diagram shows the principle of the froth flotation process.
Mineral particles suspended in froth
Froth separation
Oil and detergent recycled
Gangue
Desired product
111