Page 36 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 36
Condensation polymers
The alternative to addition polymerisation is called condensation polymerisation. In this process, each stage in the polymer chain forms as a water molecule is expelled.
Many common fibres are formed by condensation polymerisation, including nylon and polyester. Their structures are shown here and the way they are made is shown on the following pages.
Nylon
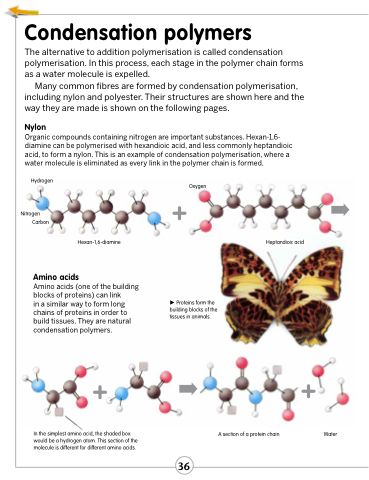
Organic compounds containing nitrogen are important substances. Hexan-1,6- diamine can be polymerised with hexandioic acid, and less commonly heptandioic acid, to form a nylon. This is an example of condensation polymerisation, where a water molecule is eliminated as every link in the polymer chain is formed.
Hydrogen
Nitrogen Carbon
Oxygen
+ ➡ Heptandioic acid
Hexan-1,6-diamine
Amino acids
Amino acids (one of the building blocks of proteins) can link
in a similar way to form long chains of proteins in order to build tissues. They are natural condensation polymers.
+
In the simplest amino acid, the shaded box would be a hydrogen atom. This section of the molecule is different for different amino acids.
Proteins form the building blocks of the tissues in animals.
➡+ A section of a protein chain
Water
36
36