Page 10 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 10
The carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the name given to the way that carbon is transferred between plants, animals, the atmosphere, rocks and oceans.
The carbon cycle is crucial to the way the planet works. It is a very complicated cycle, of which a simplified form is shown here.
The main reservoirs of carbon
are in the air (in the form of carbon dioxide) and in rocks (either as limestone and chalk or as oil, natural gas and coal). The main transfers occur through the growth and death of plants (involving the chemical processes
of photosynthesis, respiration and oxidation) and through the way people burn fossil fuels (involving the process of oxidation).
Animals
The proteins created by plants are used to make the tissues of animals, and they also provide sources of sugars, starches and fats. To release energy locked up
as glucose, the sugars, starches and
fats are combined with oxygen (they are oxidised). As sugars are oxidised, carbon dioxide and water are returned to the environment as part of the carbon cycle. As cells wear out or die, they are broken down into carbon dioxide, water and other simple compounds.
For the most part, plant and
animal tissues are broken down by decomposing organisms and the elements returned to the environment for reuse. However, in some cases, tissues are not immediately broken down and recycled, but get buried and are preserved. This produces a store of energy in the form of fossil fuels. In this case the carbon cycle is interrupted until the fuels are burned or until erosion exposes them at the surface, at which point they oxidise.
Respiration
All animals produce carbon dioxide in their lungs. The lungs breathe in air containing oxygen and expel air containing carbon dioxide. This is called respiration.
Plants release carbon dioxide gas as they convert sugars for energy. This is also respiration.
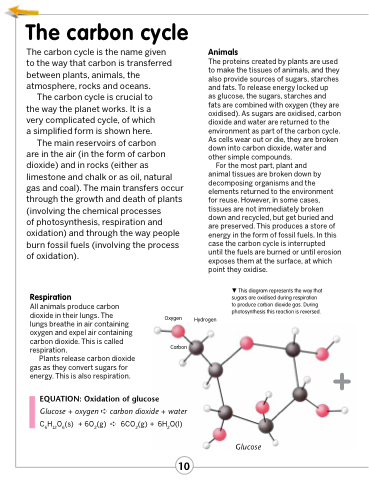
This diagram represents the way that sugars are oxidised during respiration to produce carbon dioxide gas. During photosynthesis this reaction is reversed.
Oxygen
Carbon
Glucose + oxygen ➪ carbon dioxide + water C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) ➪ 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
Hydrogen
EQUATION: Oxidation of glucose
+
Glucose
10
10