Page 11 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 11
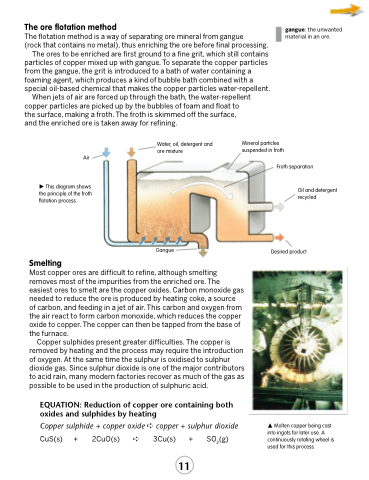
The ore flotation method
The flotation method is a way of separating ore mineral from gangue
(rock that contains no metal), thus enriching the ore before final processing. The ores to be enriched are first ground to a fine grit, which still contains
particles of copper mixed up with gangue. To separate the copper particles from the gangue, the grit is introduced to a bath of water containing a foaming agent, which produces a kind of bubble bath combined with a special oil-based chemical that makes the copper particles water-repellent.
When jets of air are forced up through the bath, the water-repellent copper particles are picked up by the bubbles of foam and float to the surface, making a froth. The froth is skimmed off the surface, and the enriched ore is taken away for refining.
gangue: the unwanted material in an ore.
Water, oil, detergent and ore mixture
Mineral particles suspended in froth
Air
This diagram shows the principle of the froth flotation process.
Smelting
Gangue
Froth separation
Oil and detergent recycled
Desired product
Most copper ores are difficult to refine, although smelting removes most of the impurities from the enriched ore. The easiest ores to smelt are the copper oxides. Carbon monoxide gas needed to reduce the ore is produced by heating coke, a source of carbon, and feeding in a jet of air. This carbon and oxygen from the air react to form carbon monoxide, which reduces the copper oxide to copper. The copper can then be tapped from the base of the furnace.
Copper sulphides present greater difficulties. The copper is removed by heating and the process may require the introduction of oxygen. At the same time the sulphur is oxidised to sulphur dioxide gas. Since sulphur dioxide is one of the major contributors to acid rain, many modern factories recover as much of the gas as possible to be used in the production of sulphuric acid.
EQUATION: Reduction of copper ore containing both oxides and sulphides by heating
Copper sulphide + copper oxide ➪ copper + sulphur dioxide
Molten copper being cast
CuS(s) + 2CuO(s) ➪ 3Cu(s)
into ingots for later use. A
+ SO2(g) continuously rotating wheel is
used for this process.
11
11