Page 13 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 13
dissolve: to break down a substance in a solution without reacting.
solution: a mixture of a liquid and at least one other substance.
weathering: the slow natural processes that break down rocks and reduce them to small fragments either by mechanical or chemical means.
The faster effects of pollution
Weathering is an example of a general chemical process called corrosion. But in urban areas, and those suffering from acid rain, carbon dioxide is not the only gas in
the rainwater. Sulphur dioxide and several oxides of nitrogen are also present. These pollutants are produced by burning fossil fuels. They produce a more concentrated acid, and the weathering effect is much more rapid.
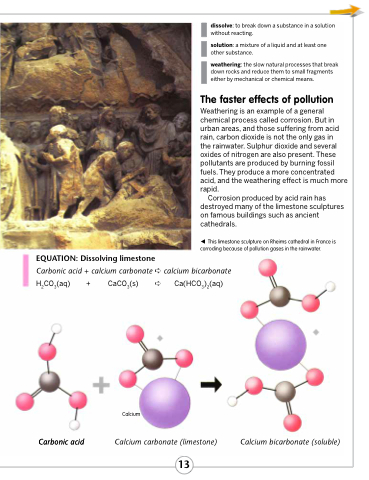
Corrosion produced by acid rain has destroyed many of the limestone sculptures on famous buildings such as ancient cathedrals.
This limestone sculpture on Rheims cathedral in France is corroding because of pollution gases in the rainwater.
EQUATION: Dissolving limestone
Carbonic acid + calcium carbonate ➪ calcium bicarbonate
H2CO3(aq) +
CaCO3(s) ➪ Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
Carbonic acid
Calcium
Calcium carbonate (limestone)
13 13
Calcium bicarbonate (soluble)