Page 15 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 15
Manufacture of hydrogen from brine
This method uses an electrical method for collecting hydrogen as part of a complicated reaction that yields a number of other important chemicals and uses cheap raw materials.
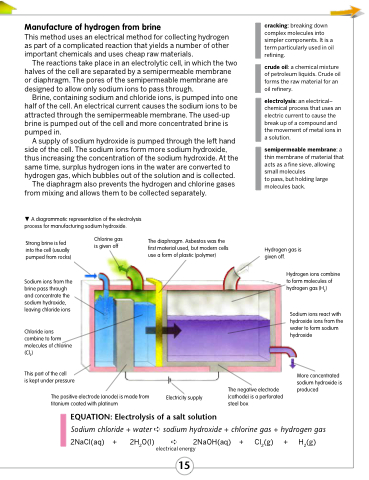
The reactions take place in an electrolytic cell, in which the two halves of the cell are separated by a semipermeable membrane or diaphragm. The pores of the semipermeable membrane are designed to allow only sodium ions to pass through.
Brine, containing sodium and chloride ions, is pumped into one half of the cell. An electrical current causes the sodium ions to be attracted through the semipermeable membrane. The used-up brine is pumped out of the cell and more concentrated brine is pumped in.
A supply of sodium hydroxide is pumped through the left hand side of the cell. The sodium ions form more sodium hydroxide, thus increasing the concentration of the sodium hydroxide. At the same time, surplus hydrogen ions in the water are converted to hydrogen gas, which bubbles out of the solution and is collected.
The diaphragm also prevents the hydrogen and chlorine gases from mixing and allows them to be collected separately.
A diagrammatic representation of the electrolysis process for manufacturing sodium hydroxide.
cracking: breaking down complex molecules into simpler components. It is a term particularly used in oil refining.
crude oil: a chemical mixture of petroleum liquids. Crude oil forms the raw material for an oil refinery.
electrolysis: an electrical– chemical process that uses an electric current to cause the break up of a compound and the movement of metal ions in a solution.
semipermeable membrane: a thin membrane of material that acts as a fine sieve, allowing small molecules
to pass, but holding large molecules back.
Hydrogen gas is given off.
Hydrogen ions combine to form molecules of hydrogen gas (H2)
Sodium ions react with hydroxide ions from the water to form sodium hydroxide
More concentrated
sodium hydroxide is The negative electrode produced
(cathode) is a perforated steel box
Strong brine is fed into the cell (usually pumped from rocks)
Sodium ions from the brine pass through and concentrate the sodium hydroxide, leaving chloride ions
Chloride ions combine to form molecules of chlorine (Cl2)
This part of the cell
is kept under pressure
Chlorine gas is given off
The diaphragm. Asbestos was the first material used, but modern cells use a form of plastic (polymer)
The positive electrode (anode) is made from titanium coated with platinum
Electricity supply
EQUATION: Electrolysis of a salt solution
Sodium chloride + water ➪ sodium hydroxide + chlorine gas + hydrogen gas 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) ➪ 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
electrical energy
15