Page 24 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 24
Lead (Pb)
Element 82. A soft, bluish-white metal in group 4 (the carbon group) in the Periodic Table.
Lead is very dense, soft and easily shaped. However, it is a relatively poor conductor of electricity.When lead is exposed to the air, it quickly develops
a coating that makes it dull brown.This coating (similar in effect to the coating that develops on copper) then helps prevent further reaction, and corrosion happens very slowly.
It is also used in low-melting- point alloys, such as solder, and in pewter. Lead will absorb sound and radiation, so it is used for soundproofing and as a protection against radiation. It was also once used as an antiknock ingredient in petrol, but lead is poisonous and so has been taken out of petrol and is no longer used in water pipes.
Lead is mainly found in the mineral lead sulphide (also called galena).
Key facts...
Name: lead
Symbol: Pb
Atomic number: 82
Atomic weight: 207.2
Position in Periodic Table: group 4 (14)
(carbon group); period 6
State at room temperature: solid
Colour: bluish-white
Density of solid: 11.3 g/cc
Melting point: 327°C
Boiling point: 1,744°C
Origin of name: from the Anglo-Saxon word
lead; the symbol is from the Latin, plumbum,
meaning liquid silver
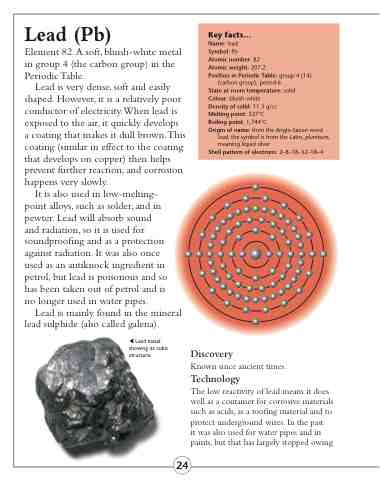
Shell pattern of electrons: 2–8–18–32–18–4
Lead metal showing its cubic structure.
Discovery
Known since ancient times.
Technology
The low reactivity of lead means it does well as a container for corrosive materials such as acids, as a roofing material and to protect underground wires. In the past
it was also used for water pipes and in paints, but that has largely stopped owing
24