Page 46 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 46
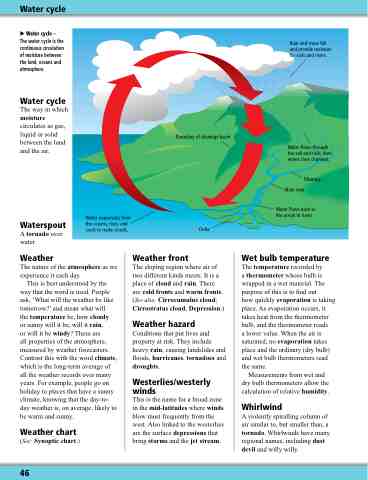
Water cycle
Rain and snow fall and provide moisture for soils and rivers.
Boundary of drainage basin
Water evaporates from the oceans, rises, and cools to make clouds.
Water flows through the soil and rock, then enters river channels.
Tributary Main river
Water flows back to the ocean in rivers.
Delta
Water cycle – The water cycle is the continuous circulation of moisture between the land, oceans and atmosphere.
Water cycle
The way in which
moisture
circulates as gas, liquid or solid between the land and the air.
Waterspout
A tornado over water.
Weather
The nature of the atmosphere as we experience it each day.
This is best understood by the way that the word is used. People ask, ‘What will the weather be like tomorrow?’ and mean what will
the temperature be, how cloudy
or sunny will it be, will it rain,
or will it be windy? These are
all properties of the atmosphere, measured by weather forecasters. Contrast this with the word climate, which is the long-term average of all the weather records over many years. For example, people go on holiday to places that have a sunny climate, knowing that the day-to- day weather is, on average, likely to be warm and sunny.
Weather chart
(See: Synoptic chart.) 46
Weather front
The sloping region where air of two different kinds meets. It is a place of cloud and rain. There are cold fronts and warm fronts. (See also: Cirrocumulus cloud; Cirrostratus cloud; Depression.)
Weather hazard
Conditions that put lives and property at risk. They include heavy rain, causing landslides and floods, hurricanes, tornadoes and droughts.
Westerlies/westerly winds
This is the name for a broad zone in the mid-latitudes where winds blow most frequently from the west. Also linked to the westerlies are the surface depressions that bring storms and the jet stream.
Wet bulb temperature
The temperature recorded by
a thermometer whose bulb is wrapped in a wet material. The purpose of this is to find out
how quickly evaporation is taking place. As evaporation occurs, it takes heat from the thermometer bulb, and the thermometer reads
a lower value. When the air is saturated, no evaporation takes place and the ordinary (dry bulb) and wet bulb thermometers read the same.
Measurements from wet and dry bulb thermometers allow the calculation of relative humidity.
Whirlwind
A violently spiralling column of air similar to, but smaller than, a tornado. Whirlwinds have many regional names, including dust devil and willy willy.