Page 55 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 55
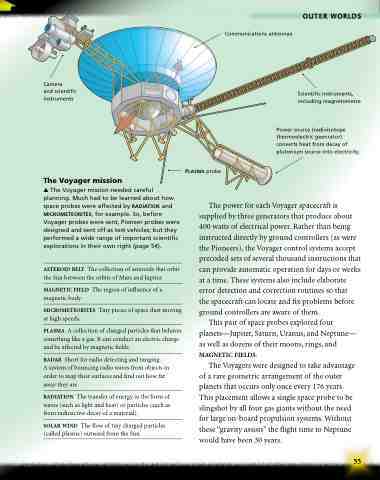
Camera
and scientific instruments
Scientific instruments, including magnetometre
Power source (radioisotope thermoelectric geenrator) converts heat from decay of plutonium source into electricity.
The Voyager mission
The Voyager mission needed careful planning. Much had to be learned about how space probes were affected by radiaTion and micromeTeoriTes, for example. So, before Voyager probes were sent, Pioneer probes were designed and sent off as test vehicles; but they performed a wide range of important scientific explorations in their own right (page 5).
asteroid belt The collection of asteroids that orbit the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
magnetic field The region of influence of a magnetic body.
The power for each Voyager spacecraft is supplied by three generators that produce about 400 watts of electrical power. Rather than being instructed directly by ground controllers (as were the Pioneers), the Voyager control systems accept precoded sets of several thousand instructions that can provide automatic operation for days or weeks at a time. These systems also include elaborate error detection and correction routines so that
the spacecraft can locate and fix problems before ground controllers are aware of them.
This pair of space probes explored four planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune— as well as dozens of their moons, rings, and magnetic fields.
The Voyagers were designed to take advantage of a rare geometric arrangement of the outer planets that occurs only once every 176 years. This placement allows a single space probe to be slingshot by all four gas giants without the need for large on-board propulsion systems. Without these “gravity assists” the flight time to Neptune would have been 30 years.
micrometeorites
at high speeds.
Tiny pieces of space dust moving
plasma A collection of charged particles that behaves something like a gas. It can conduct an electric charge and be affected by magnetic fields.
radar Short for radio detecting and ranging.
A system of bouncing radio waves from objects in order to map their surfaces and find out how far away they are.
radiation The transfer of energy in the form of waves (such as light and heat) or particles (such as from radioactive decay of a material).
solar wind The flow of tiny charged particles (called plasma) outward from the Sun.
Plasma probe
Communications antennae
55