Page 16 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 16
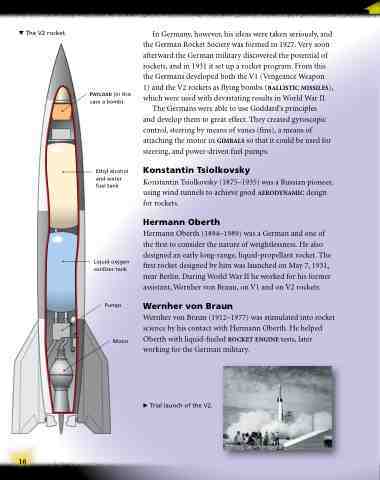
The V2 rocket.
In Germany, however, his ideas were taken seriously, and the German Rocket Society was formed in 1927. Very soon afterward the German military discovered the potential of rockets, and in 1931 it set up a rocket program. From this the Germans developed both the V1 (Vengeance Weapon 1) and the V2 rockets as flying bombs (ballistic missiles), which were used with devastating results in World War II.
The Germans were able to use Goddard’s principles
and develop them to great effect. They created gyroscopic control, steering by means of vanes (fins), a means of attaching the motor in gimbals so that it could be used for steering, and power-driven fuel pumps.
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (1875–1935) was a Russian pioneer, using wind tunnels to achieve good aerodynamic design for rockets.
Hermann Oberth
Hermann Oberth (1894–1989) was a German and one of the first to consider the nature of weightlessness. He also designed an early long-range, liquid-propellant rocket. The first rocket designed by him was launched on May 7, 1931, near Berlin. During World War II he worked for his former assistant, Wernher von Braun, on V1 and on V2 rockets.
Wernher von Braun
Wernher von Braun (1912–1977) was stimulated into rocket science by his contact with Hermann Oberth. He helped Oberth with liquid-fueled rocket engine tests, later working for the German military.
Trial launch of the V2.
Payload (in this case a bomb)
Ethyl alcohol and water fuel tank
Liquid oxygen oxidizer tank
Pumps
Motor
16