Page 56 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 56
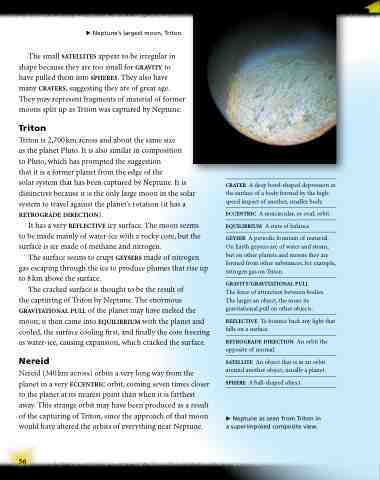
Neptune’s largest moon, Triton.
The small satellites appear to be irregular in shape because they are too small for gravity to have pulled them into spheres. They also have many craters, suggesting they are of great age. They may represent fragments of material of former moons split up as Triton was captured by Neptune.
Triton
Triton is 2,700 km across and about the same size
as the planet Pluto. It is also similar in composition
to Pluto, which has prompted the suggestion
that it is a former planet from the edge of the
solar system that has been captured by Neptune. It is distinctive because it is the only large moon in the solar system to travel against the planet’s rotation (it has a retrograde direction).
It has a very reflective icy surface. The moon seems to be made mainly of water-ice with a rocky core, but the surface is ice made of methane and nitrogen.
The surface seems to erupt geysers made of nitrogen gas escaping through the ice to produce plumes that rise up to 8 km above the surface.
The cracked surface is thought to be the result of
the capturing of Triton by Neptune. The enormous gravitational pull of the planet may have melted the moon; it then came into equilibrium with the planet and cooled, the surface cooling first, and finally the core freezing as water-ice, causing expansion, which cracked the surface.
Nereid
Nereid (340 km across) orbits a very long way from the planet in a very eccentric orbit, coming seven times closer to the planet at its nearest point than when it is farthest away. This strange orbit may have been produced as a result of the capturing of Triton, since the approach of that moon would have altered the orbits of everything near Neptune.
crater A deep bowl-shaped depression in the surface of a body formed by the high- speed impact of another, smaller body.
eccentric A noncircular, or oval, orbit.
equilibrium A state of balance.
geyser A periodic fountain of material. On Earth geysers are of water and steam, but on other planets and moons they are formed from other substances, for example, nitrogen gas on Triton.
gravity/gravitational pull
The force of attraction between bodies. The larger an object, the more its gravitational pull on other objects.
reflective To bounce back any light that falls on a surface.
retrograde direction An orbit the opposite of normal.
satellite An object that is in an orbit around another object, usually a planet.
sphere A ball-shaped object.
Neptune as seen from Triton in a superimposed composite view.
56