Page 18 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 18
Evaporation and condensation
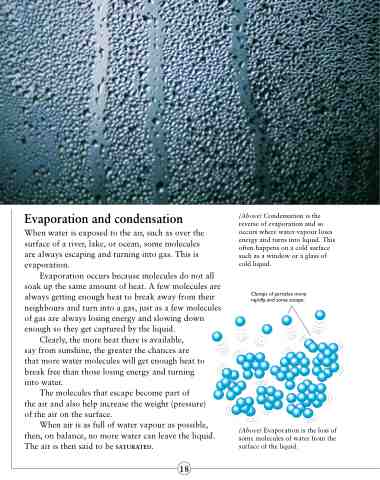
When water is exposed to the air, such as over the surface of a river, lake, or ocean, some molecules are always escaping and turning into gas. This is evaporation.
Evaporation occurs because molecules do not all soak up the same amount of heat. A few molecules are always getting enough heat to break away from their neighbours and turn into a gas, just as a few molecules of gas are always losing energy and slowing down enough so they get captured by the liquid.
Clearly, the more heat there is available,
say from sunshine, the greater the chances are that more water molecules will get enough heat to break free than those losing energy and turning into water.
The molecules that escape become part of
the air and also help increase the weight (pressure) of the air on the surface.
When air is as full of water vapour as possible, then, on balance, no more water can leave the liquid. The air is then said to be saturated.
(Above) Condensation is the reverse of evaporation and so occurs where water vapour loses energy and turns into liquid. This often happens on a cold surface such as a window or a glass of cold liquid.
Clumps of particles move rapidly, and some escape.
(Above) Evaporation is the loss of some molecules of water from the surface of the liquid.
18