Page 15 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 15
EQUATION: Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water ➪ glucose + oxygen 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) ➪ C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g)
EQUATION: Oxidation of organic matter
Glucose + oxygen ➪ carbon dioxide + water C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) ➪ 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
combustion: the special case of oxidisation of
a substance where a considerable amount of heat and usually light are given out. Combustion is often referred to as “burning”.
exothermic reaction: a reaction that gives heat to the surroundings. Many oxidation reactions, for example, give out heat.
photosynthesis: the process by which plants use the energy of the Sun to make the compounds they need for life. In photosynthesis, six molecules of carbon dioxide from the air combine with six molecules of water, forming one molecule of glucose (sugar) and releasing six molecules of
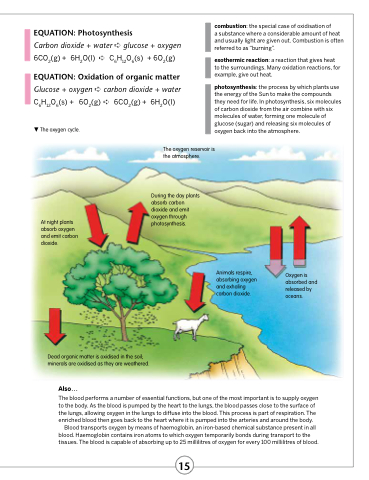
The oxygen cycle.
oxygen back into the atmosphere.
At night plants absorb oxygen and emit carbon dioxide.
The oxygen reservoir is the atmosphere.
During the day plants absorb carbon dioxide and emit oxygen through photosynthesis.
Dead organic matter is oxidised in the soil; minerals are oxidised as they are weathered.
Animals respire, absorbing oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide.
Oxygen is absorbed and released by oceans.
Also...
The blood performs a number of essential functions, but one of the most important is to supply oxygen to the body. As the blood is pumped by the heart to the lungs, the blood passes close to the surface of the lungs, allowing oxygen in the lungs to diffuse into the blood. This process is part of respiration. The enriched blood then goes back to the heart where it is pumped into the arteries and around the body.
Blood transports oxygen by means of haemoglobin, an iron-based chemical substance present in all blood. Haemoglobin contains iron atoms to which oxygen temporarily bonds during transport to the tissues. The blood is capable of absorbing up to 25 millilitres of oxygen for every 100 millilitres of blood.
15
15