Page 23 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 23
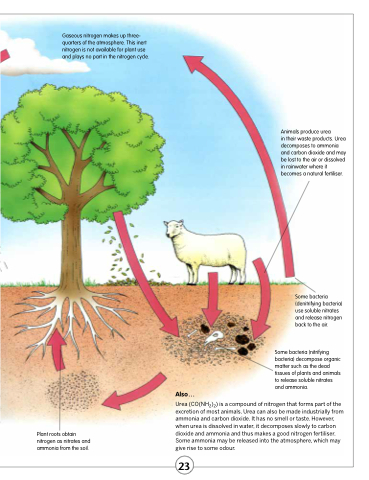
Gaseous nitrogen makes up three- quarters of the atmosphere. This inert nitrogen is not available for plant use and plays no part in the nitrogen cycle.
Animals produce urea
in their waste products. Urea decomposes to ammonia and carbon dioxide and may be lost to the air or dissolved in rainwater where it becomes a natural fertiliser.
Plant roots obtain nitrogen as nitrates and ammonia from the soil.
Urea (CO(NH2)2) is a compound of nitrogen that forms part of the excretion of most animals. Urea can also be made industrially from ammonia and carbon dioxide. It has no smell or taste. However, when urea is dissolved in water, it decomposes slowly to carbon dioxide and ammonia and thus makes a good nitrogen fertiliser. Some ammonia may be released into the atmosphere, which may give rise to some odour.
Also...
Some bacteria (denitrifying bacteria) use soluble nitrates and release nitrogen back to the air.
Some bacteria (nitrifying bacteria) decompose organic matter such as the dead tissues of plants and animals to release soluble nitrates and ammonia.
23
23