Page 15 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 15
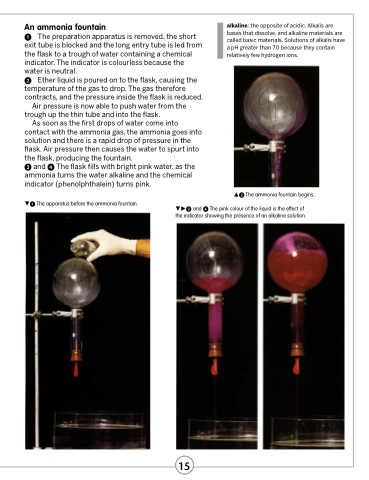
An ammonia fountain
The preparation apparatus is removed, the short exit tube is blocked and the long entry tube is led from the flask to a trough of water containing a chemical indicator. The indicator is colourless because the water is neutral.
Ether liquid is poured on to the flask, causing the temperature of the gas to drop. The gas therefore contracts, and the pressure inside the flask is reduced.
Air pressure is now able to push water from the trough up the thin tube and into the flask.
As soon as the first drops of water come into contact with the ammonia gas, the ammonia goes into solution and there is a rapid drop of pressure in the flask. Air pressure then causes the water to spurt into the flask, producing the fountain.
and The flask fills with bright pink water, as the ammonia turns the water alkaline and the chemical indicator (phenolphthalein) turns pink.
alkaline: the opposite of acidic. Alkalis are bases that dissolve, and alkaline materials are called basic materials. Solutions of alkalis have a pH greater than 7.0 because they contain relatively few hydrogen ions.
The apparatus before the ammonia fountain.
The ammonia fountain begins. and The pink colour of the liquid is the effect of
the indicator showing the presence of an alkaline solution.
15
15