Page 28 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 28
Variety in organic compounds
Carbon chemistry relies heavily on the use of hydrocarbon products obtained from petroleum. On these two pages you can see the structure of some common hydrocarbon substances.
Alkanes (paraffins)
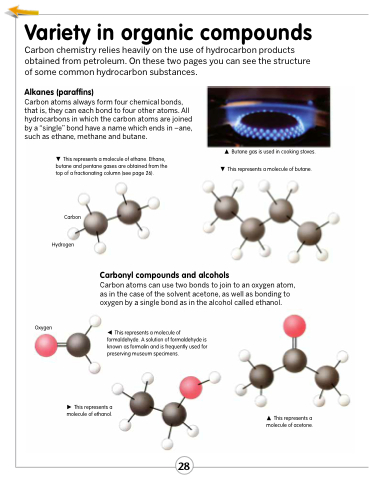
Carbon atoms always form four chemical bonds, that is, they can each bond to four other atoms. All hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by a “single” bond have a name which ends in –ane, such as ethane, methane and butane.
This represents a molecule of ethane. Ethane, butane and pentane gases are obtained from the top of a fractionating column (see page 26).
Butane gas is used in cooking stoves. This represents a molecule of butane.
Oxygen
This represents a molecule of formaldehyde. A solution of formaldehyde is known as formalin and is frequently used for preserving museum specimens.
This represents a molecule of ethanol.
Carbon
Hydrogen
Carbonyl compounds and alcohols
Carbon atoms can use two bonds to join to an oxygen atom, as in the case of the solvent acetone, as well as bonding to oxygen by a single bond as in the alcohol called ethanol.
This represents a molecule of acetone.
28
28