Page 33 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 33
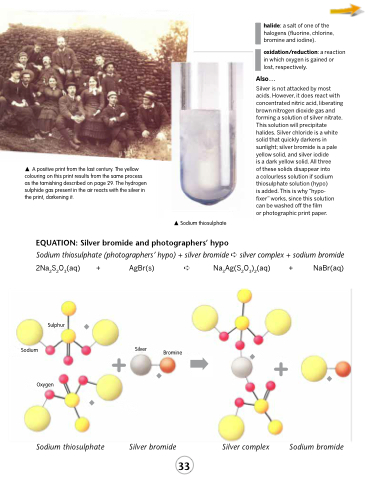
A positive print from the last century. The yellow colouring on this print results from the same process as the tarnishing described on page 29. The hydrogen sulphide gas present in the air reacts with the silver in the print, darkening it.
halide: a salt of one of the halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine).
oxidation/reduction: a reaction in which oxygen is gained or lost, respectively.
Also...
Silver is not attacked by most acids. However, it does react with concentrated nitric acid, liberating brown nitrogen dioxide gas and forming a solution of silver nitrate. This solution will precipitate halides. Silver chloride is a white solid that quickly darkens in sunlight; silver bromide is a pale yellow solid, and silver iodide
is a dark yellow solid. All three
of these solids disappear into
a colourless solution if sodium thiosulphate solution (hypo)
is added. This is why “hypo-
fixer” works, since this solution can be washed off the film
or photographic print paper.
EQUATION: Silver bromide and photographers’ hypo
2Na2S2O3(aq)
Sulphur Sodium
Oxygen
+ AgBr(s)
➪ Na3Ag(S2O3)2(aq) + NaBr(aq)
Bromine ➡ ◆ +
Silver complex Sodium bromide
Sodium thiosulphate
◆
◆
+ Silver
Silver bromide
Sodium thiosulphate
Sodium thiosulphate (photographers’ hypo) + silver bromide ➪ silver complex + sodium bromide
◆
◆
33
33