Page 15 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 15
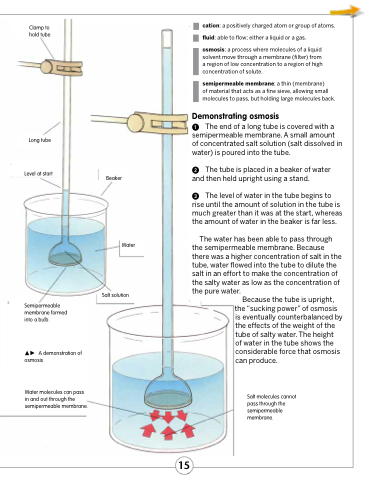
Clamp to hold tube
cation: a positively charged atom or group of atoms.
fluid: able to flow; either a liquid or a gas.
osmosis: a process where molecules of a liquid solvent move through a membrane (filter) from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration of solute.
semipermeable membrane: a thin (membrane)
of material that acts as a fine sieve, allowing small molecules to pass, but holding large molecules back.
Demonstrating osmosis
The end of a long tube is covered with a semipermeable membrane. A small amount of concentrated salt solution (salt dissolved in water) is poured into the tube.
The tube is placed in a beaker of water and then held upright using a stand.
The level of water in the tube begins to rise until the amount of solution in the tube is much greater than it was at the start, whereas the amount of water in the beaker is far less.
The water has been able to pass through the semipermeable membrane. Because there was a higher concentration of salt in the tube, water flowed into the tube to dilute the salt in an effort to make the concentration of the salty water as low as the concentration of the pure water.
Because the tube is upright, the “sucking power” of osmosis
is eventually counterbalanced by the effects of the weight of the tube of salty water. The height
of water in the tube shows the considerable force that osmosis can produce.
Salt molecules cannot pass through the semipermeable membrane.
Long tube
Level at start
Beaker
Water
Salt solution
Semipermeable membrane formed into a bulb.
A demonstration of osmosis
Water molecules can pass in and out through the semipermeable membrane.
15 15