Page 31 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 31
Bromine (Br)
Element 35. Bromine is one of the halogens in group 7 in the Periodic Table. It is the only liquid non-metallic element. An amber–brown gas, it is highly poisonous.
Discovery
In 1826 the French chemist Antoine-Jérôme Balard discovered bromine as a compound in salt left after the evaporation of sea water. Bromine is still obtained commercially from sea water.
Technology
Bromine compounds (bromides) are common in photography. Bromine is a bleaching agent and is used as a flame retardant, especially for plastics.
Tyrian purple is a dye made from a type of clam in which there is a high concentration of bromine.
Geology
Bromine is not found as a native element but as a bromide in
sea water.A small number
of minerals also contain
the bromide, especially evaporites that were formed by evaporation of sea water.
Biology
Bromine is a trace element in
animals; but when present in
too much concentration, it causes depression. If inhaled as a vapour, bromine is extremely poisonous, affecting the eyes and throat. It produces sores on the skin. It goes into compounds as a sedative in medicine and as a pesticide against insects. Bromine also helps in water purification.
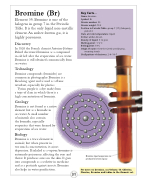
Bromine liquid evaporates to produce bromine vapour.
Key facts...
Name: bromine
Symbol: Br
Atomic number: 35
Atomic weight: 79.9
Position in Periodic Table: group 7 (17) (halogens);
period 4
State at room temperature: liquid
Colour: amber–brown
Density of liquid: 3.12 g/cc
Melting point: –7.2°C
Boiling point: 59°C
Origin of name: from the Greek word bromos,
meaning stench
Shell pattern of electrons: 2–8–18–7
For more on bromine, see Volume 14: Chlorine, Fluorine, Bromine and Iodine in the Elements set.
31