Page 38 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the window or tab.
P. 38
38
reach hundreds of kilometres from the fissure from which they were erupted.
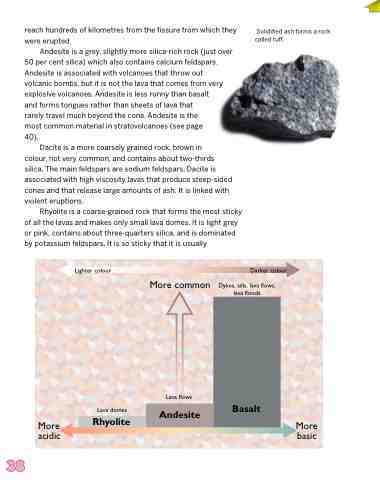
Andesite is a grey, slightly more silica-rich rock (just over 50 per cent silica) which also contains calcium feldspars. Andesite is associated with volcanoes that throw out volcanic bombs, but it is not the lava that comes from very explosive volcanoes. Andesite is less runny than basalt
and forms tongues rather than sheets of lava that
rarely travel much beyond the cone. Andesite is the
most common material in stratovolcanoes (see page
40).
Dacite is a more coarsely grained rock, brown in
colour, not very common, and contains about two-thirds silica. The main feldspars are sodium feldspars. Dacite is associated with high viscosity lavas that produce steep-sided cones and that release large amounts of ash. It is linked with violent eruptions.
Rhyolite is a coarse-grained rock that forms the most sticky of all the lavas and makes only small lava domes. It is light grey or pink, contains about three-quarters silica, and is dominated by potassium feldspars. It is so sticky that it is usually
Solidified ash forms a rock called tuff.
More acidic
More basic
Lighter colour
Darker colour
Dykes, sills, lava flows, lava floods
Lava domes
Rhyolite
Lava flows
Andesite
Basalt
More common