Page 43 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 43
Soil erosion
Slaty cleavage
A characteristic pattern found in slates in which the parallel arrangement of clay minerals causes the rock to fracture (cleave) in sheets.
Soil erosion
The accelerated movement of soil away from a field by wind or heavy rain. Soil erosion is usually a human problem caused by poor farming methods, especially by
leaving the soil uncovered between harvesting and the growth of a new crop. (See also: Erode, erosion and Gulleying.)
Soil
A mixture of mineral and organic matter that forms on the surface of most rocks. It is the medium in which plants grow.
Soils are divided up into major soil groups based on the processes at work inside the soil.
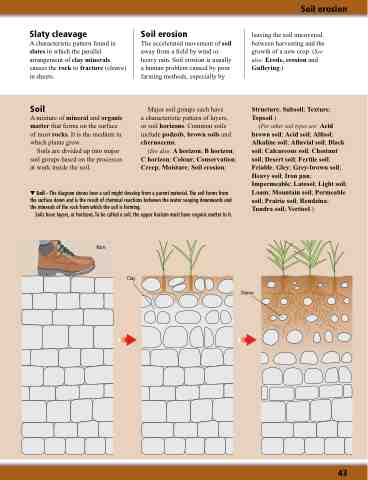
Soil – The diagram shows how a soil might the surface down and is the result of chemical the minerals of the rock from which the soil is
Soils have layers, or horizons. To be called a
Rain
Major soil groups each have
a characteristic pattern of layers, or soil horizons. Common soils include podzols, brown soils and chernozems.
(See also: A horizon; B horizon; C horizon; Colour; Conservation; Creep; Moisture; Soil erosion;
develop from a parent material. The soil forms from reactions between the water seeping downwards and forming.
soil, the upper horizon must have organic matter in it.
Clay
Structure; Subsoil; Texture; Topsoil.)
(For other soil types see: Acid brown soil; Acid soil; Alfisol; Alkaline soil; Alluvial soil; Black soil; Calcareous soil; Chestnut soil; Desert soil; Fertile soil; Friable; Gley; Grey-brown soil; Heavy soil; Iron pan; Impermeable; Latosol; Light soil; Loam; Mountain soil; Permeable soil; Prairie soil; Rendzina; Tundra soil; Vertisol.)
Stones
43