Page 22 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 22
Fracture
Fracture
A substantial break across a rock. Some crystals break irregularly, rather than in a single direction. This indicates that the crystal
has no special lines of weakness. A curved fracture is known as
a conchoidal fracture. Flint and glass show conchoidal fracture. (See also: Fracture zone and Slaty cleavage.)
Fracture zone
A region of rock in which fractures are common. Fracture zones are particularly common in folded rock and near faults. (See also: Normal fault and Reversed fault).
Fracture zones are places where rocks have been broken and are more liable to erode. Fracture zones are often connected with bands of low land. River valleys sometimes follow fracture zones.
Friable
Used to describe soil that naturally breaks up into small clumps (crumb structure). It refers to a loamy soil or a clay soil with a good calcium content.
Fuel
Any material that can be used
to produce heat energy. The main fuels in use today are called fossil fuels – coal, oil and natural gas. They are called fossil fuels because they were formed in the geological past and are not forming in such abundance today.
G
Gabbro
An alkaline igneous rock, typically showing dark-coloured crystals. It is made of the same minerals as basalt, but it has large
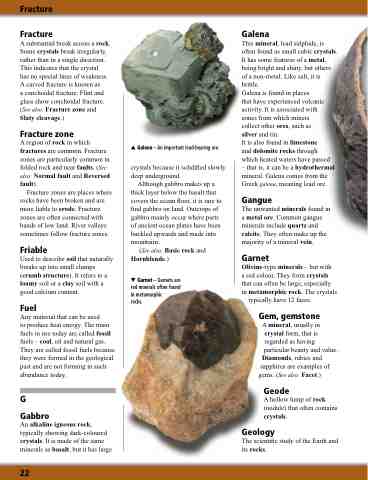
Galena – An important lead-bearing ore.
crystals because it solidified slowly deep underground.
Although gabbro makes up a thick layer below the basalt that covers the ocean floor, it is rare to find gabbro on land. Outcrops of gabbro mainly occur where parts of ancient ocean plates have been buckled upwards and made into mountains.
(See also: Basic rock and Hornblende.)
Garnet – Garnets are red minerals often found in metamorphic
rocks.
Galena
This mineral, lead sulphide, is often found as small cubic crystals. It has some features of a metal, being bright and shiny, but others of a non-metal. Like salt, it is brittle.
Galena is found in places
that have experienced volcanic activity. It is associated with
zones from which miners
collect other ores, such as
silver and tin.
It is also found in limestone
and dolomite rocks through
which heated waters have passed
– that is, it can be a hydrothermal mineral. Galena comes from the Greek galena, meaning lead ore.
Gangue
The unwanted minerals found in a metal ore. Common gangue minerals include quartz and calcite. They often make up the majority of a mineral vein.
Garnet
Olivine-type minerals – but with
a red colour. They form crystals that can often be large, especially in metamorphic rock. The crystals
typically have 12 faces.
Gem, gemstone
A mineral, usually in crystal form, that is regarded as having particular beauty and value.
Diamonds, rubies and sapphires are examples of
gems. (See also: Facet.)
Geode
A hollow lump of rock (nodule) that often contains crystals.
Geology
The scientific study of the Earth and its rocks.
22