Page 21 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 21
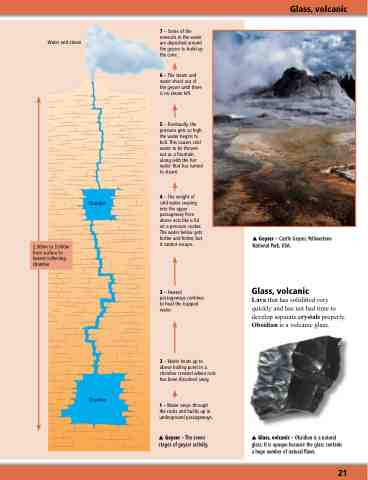
Water and steam
7 – Some of the minerals in the water are deposited around the geyser to build up the cone.
6 – The steam and water shoot out of the geyser until there is no steam left.
5 – Eventually, the pressure gets so high the water begins to boil. This causes cold water to be thrown out as a fountain, along with the hot water that has turned to steam.
4 – The weight of cold water seeping into the upper passageway from above acts like a lid on a pressure cooker. The water below gets hotter and hotter, but it cannot escape.
3 – Heated passageways continue to heat the trapped water.
2 – Water heats up to above boiling point in a chamber created where rock has been dissolved away.
1 – Water seeps through the rocks and builds up in underground passageways.
Geyser – The seven stages of geyser activity.
2,000m to 3,000m from surface to lowest collecting chamber
Geyser – Castle Geyser, Yellowstone National Park, USA.
Glass, volcanic
Lava that has solidified very quickly and has not had time to develop separate crystals properly. Obsidian is a volcanic glass.
Chamber
Chamber
Glass, volcanic
Glass, volcanic – Obsidian is a natural glass. It is opaque because the glass contains a huge number of natural flaws.
21